Guide to Business Valuation
5-Second Summary
- Business Valuation is an important tool to support owner managers decision making.
- You can get a quick valuation using a free valuation calculator.
- A full DCF Company Report is more accurate and therefore ultimately more useful.
Why perform a Business Valuation?
Common reasons given for a business valuation report include;
- to set an asking price for a business sale
- construct an offer to buy a business
- get a bank loan
- write a buy-sell agreement
- settle a disagreement with a partner
- defend your business value in a legal dispute
- the owner(s) are just be curious
How do you find the “value” of the business?
There are many ways to find a value of a company, however ultimately the value of a company is only truly discovered when someone buys the business or if it is listed on the stock market. However, valuing a business is still a valuable exercise to support a wider business strategy.
What are the different types of Business Valuation?
Total Assets Value
One method totalling up the value of everything the business owns, including inventory, equipment and unpaid invoices and subtracting any debt or liabilities.
Multiples Valuation
Multiple’s valuation or relative valuation uses the known market valuation of number of peers within a sector, usually listed companies as their valuation is easily obtained. This ratio is then applied to your own company to provide an estimate of its valuation.
Multiples Valuation is therefore very much an estimate of your current valuation based on what the stock market believes are the future growth prospects of your listed peers rather than your own companies future potential.
A typical example is accountants, who have a multiple of 1.5 to 2x versus a FinTech that has multiples of 15x or more.
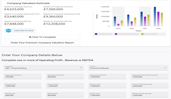
Valuation = Profit x Sector Multiple
Try our free Multiples Valuation Calculator
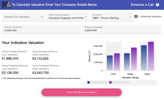
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF)
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) is generally considered the most accurate method for valuing a company. In DCF, future cash flows are estimated and then discounted by the cost of capital to give their present values. This means DCF is more about the future growth and profit than past performance.
In order to calculate DCF, you therefore need to have your current cash flow with estimates of future cash flows and your cost of capital.
In DCF, cash flows generated over the next 5 years and in perpetuity are estimated and then discounted back to what their total sum would be worth today based on a 'discount rate' - usually weighted average cost of capital (WACC) In order to calculate DCF, you therefore need to have your current cash flow with estimates of future cash flows and WACC. DCF, like multiples have their flaws too, in general, the practice of valuing a company is an imperfect science. However, it informs a basis of discussion and overall market price.
DCF Formula
DCF = [(CF1/1 + r)^1] + [(CF2/1 + r)^2] + [(CFn/1 + n)^n]
CFx = Cash Flow in year x
R = Discount rate
N = year
What is a typical Business Valuation Process?
To create a comprehensive business valuation, typical the following process is followed.
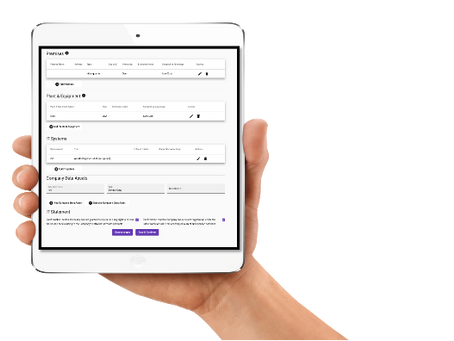
Inputs:
- 2-5 years statuary accounts
- Ideally 1-5 years forecast accounts
- Company Sector
- Default Currency
- What is the Company Growth Stage? Idea, Development, Startup, Expansion or Established
Process:
-
Inputs are feed into multiple valuation models (spreadsheet or application)
-
A map of peer companies is built using a financial data platform like S&P, Pitchbook, BVD etc.
- An Analyst pulls together and analyses the above inputs, writes commentary and creates graphs to more easily present the data.
Outputs:
-
Industry Sector Analysis
-
Market Multiples & DCF Valuation
-
Detailed Valuation Report (PDF)
What is small business valuation rule of thumb?
The most commonly used rule of thumb for a small business with under £1m in EBITDA is to multiple the EBITDA by 2x. This obviously can potentially be very inaccurate.
This is due to a small business typically being run as a lifestyle businesses meant to support the owner manager rather than being set up in a way that provides value to the market.
Larger businesses have typically been scaled and therefore have a strategic value and/or command strategic premium.
What is a Business Valuation Report?
A valuation report is a document that provides an analysis of a company's worth, often prepared by a professional appraiser or a financial institution. The purpose of the report is to determine the economic value of a business, assets, or company equity.
This report is crucial for business sales, mergers and acquisitions, investment analysis, capital budgeting, and financial reporting. It can also be important for litigation, tax assessments, and planning for estate or gift taxes.
Here are some key elements that are usually included in a valuation report:
Introduction
This section includes a brief overview of the company, including its history, location, size, and operations.
Purpose and Scope of the Valuation
This outlines the reasons for conducting the valuation and the standards used to complete the report.
Methodology
The valuation methods and approaches used in the analysis, such as the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) method, market capitalisation, market multiples, or net asset value method.
Financial Analysis
This involves a detailed review of the company's financial statements, including profit and loss accounts, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
Market and Industry Analysis
This involves a review of the market in which the company operates, including its size, growth rates, trends, competition, and regulatory environment.
Valuation
This section includes the actual value that was determined, including any assumptions or conditions that were factored into the valuation.
Commentary
The final thoughts of the report, including the assessor's final opinion of the company's value.
What are the two most popular approaches and methods for business valuation?
- Market Multiple is the most popular approach as its very quick and easy to perform, however depending on the size of the business and sector it can be misleading.
- DCF is the most accurate and therefore the most used for actual valuation during an M&A process.